Blockchain and data analytics are two of the most transformative technologies of the 21st century. When combined, they offer a powerful toolset for extracting insights from vast amounts of data in a secure and transparent manner. Let’s dive deep into the world of blockchain data analytics.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers in a way that ensures the data can only be modified upon the consensus of all participants in the system. Each record in the blockchain is called a block, and multiple blocks are linked together in a chain.
Key Features of Blockchain:
- Decentralization: Unlike centralized databases, where a single entity has control, blockchains operate on multiple computers simultaneously.
- Transparency: All participants can view the transactions.
- Immutability: Once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered.
- Security: Transactions are encrypted and must be verified by the network before being added.
What is Data Analytics?
Data Analytics is the process of examining vast datasets to extract meaningful insights. This analytical process aids organizations in making informed decisions, predicting upcoming trends, and comprehending intricate patterns within the data. The components of data analytics encompass several stages.
Initially, there’s the data collection phase where raw data is gathered from diverse sources. This is followed by data processing, which involves cleaning and organizing the data to prepare it for the analysis stage. During the analysis phase, statistical tools and algorithms are employed to derive insights from the data. Finally, data visualization techniques are used, representing the data in easily understandable formats such as graphs and charts.
Merging Blockchain and Data Analytics
When blockchain and data analytics come together, they form Blockchain Data Analytics. This involves analyzing data from blockchain networks to derive insights, predict trends, and make informed decisions.
Benefits of Blockchain Data Analytics:
- Enhanced Security: Data from blockchain networks is encrypted, ensuring that the insights derived are based on secure and verified data.
- Real-time Analysis: Blockchain operates in real-time, allowing for instantaneous data analysis.
- Transparency: The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that data analytics processes are transparent and verifiable by all participants.
Applications of Blockchain Data Analytics
Blockchain Data Analytics finds its applications in various sectors, enhancing their efficiency and transparency. In the realm of supply chain management, it plays a pivotal role in tracking products right from their manufacturing stage to their final delivery, ensuring a transparent and authentic trail. The financial services sector benefits immensely from this integration, as analyzing transaction data can lead to the detection of fraud, comprehensive risk assessment, and gaining insights into customer behaviors. Furthermore, the healthcare industry is also tapping into the potential of blockchain data analytics. It aids in verifying the authenticity of drugs, meticulously tracking patient data, and even predicting potential disease outbreaks, ensuring a more streamlined and secure healthcare system.
Challenges and Considerations
While blockchain data analytics offers numerous benefits, there are challenges:
- Data Privacy: Public blockchains are transparent, which might raise data privacy concerns.
- Scalability: As the amount of data grows, analyzing it in real-time can become challenging.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Merging blockchain data with traditional databases can be complex.
The Rise of Blockchain-Based Technologies
The 21st century has witnessed the emergence of numerous groundbreaking technologies, and among the most influential is blockchain. Its decentralized nature, combined with its potential to revolutionize various sectors, has made it a focal point of technological advancements.
The Genesis of Blockchain
Blockchain’s inception can be traced back to the conceptualization of cryptographic secured chain of blocks by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta in 1991. However, it wasn’t until 2008 that the term “blockchain” became synonymous with decentralized ledger technology, thanks to the introduction of Bitcoin by the pseudonymous entity, Satoshi Nakamoto.
Core Principles of Blockchain
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases controlled by a single entity, blockchain operates across multiple systems, ensuring no single point of control or failure.
- Transparency: Every transaction is visible to all participants, ensuring accountability.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it’s nearly impossible to alter, ensuring data integrity.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Transactions are validated by network participants through mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS).
Evolution and Growth
From its humble beginnings as the underlying technology for Bitcoin, blockchain has evolved to cater to diverse applications beyond just cryptocurrencies. The introduction of Ethereum in 2015, which introduced smart contracts, expanded blockchain’s potential applications manifold.
Growth Metrics:
- The global blockchain market size was valued at $2.89 billion in 2019.
- It’s projected to reach $137.29 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 62.7% from 2020 to 2027.
Comparison Table: Blockchain Evolution Over the Years
| Year | Key Developments | Notable Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 2008 | Introduction of Bitcoin | Cryptocurrency |
| 2015 | Launch of Ethereum | Smart Contracts |
| 2017 | ICO Boom | Fundraising via Token Sales |
| 2019 | Rise of DeFi | Decentralized Finance Platforms |
| 2021 | NFT Craze | Digital Art & Collectibles |
Diverse Applications of Blockchain
- Supply Chain: Ensures product authenticity and traceability from origin to consumer.
- Healthcare: Secure storage and sharing of medical records, ensuring patient privacy.
- Finance: Cross-border transactions, fraud detection, and transparent auditing.
- Real Estate: Transparent property transactions, reducing fraud and ensuring efficient property transfer.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite its potential, blockchain faces challenges like scalability issues, energy consumption concerns (especially with PoW), and regulatory uncertainties. However, with ongoing research and the development of solutions like Layer 2 scaling and Proof of Stake, the future of blockchain remains promising.
Understanding Blockchain and Its Significance
Blockchain, often hailed as the ‘new internet’, is a groundbreaking technology that promises to reshape the landscape of various industries. Its decentralized nature, combined with its ability to provide transparency and security, makes it a revolutionary tool in the digital age.
The Concept of Blockchain
At its core, a blockchain is a distributed ledger or database that records transactions in a series of blocks. These blocks are linked and secured using cryptographic principles, ensuring that once data is added to the blockchain, it becomes nearly immutable.
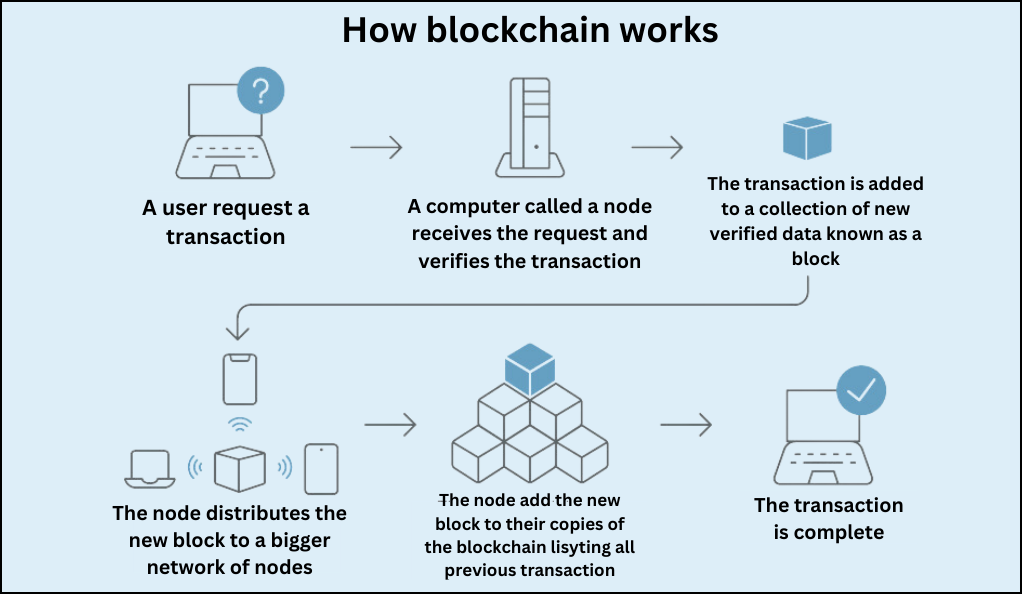
How Does Blockchain Work?
- Transaction Initiation: A user initiates a transaction, which is then broadcasted to a network of peer nodes.
- Verification: The network of nodes validates the transaction using consensus algorithms.
- Block Creation: Once verified, the transaction is packaged into a block.
- Block Addition: This block is then added to the chain in a linear, chronological order.
- Completion: The transaction is now complete, and the blockchain has an updated record of it.
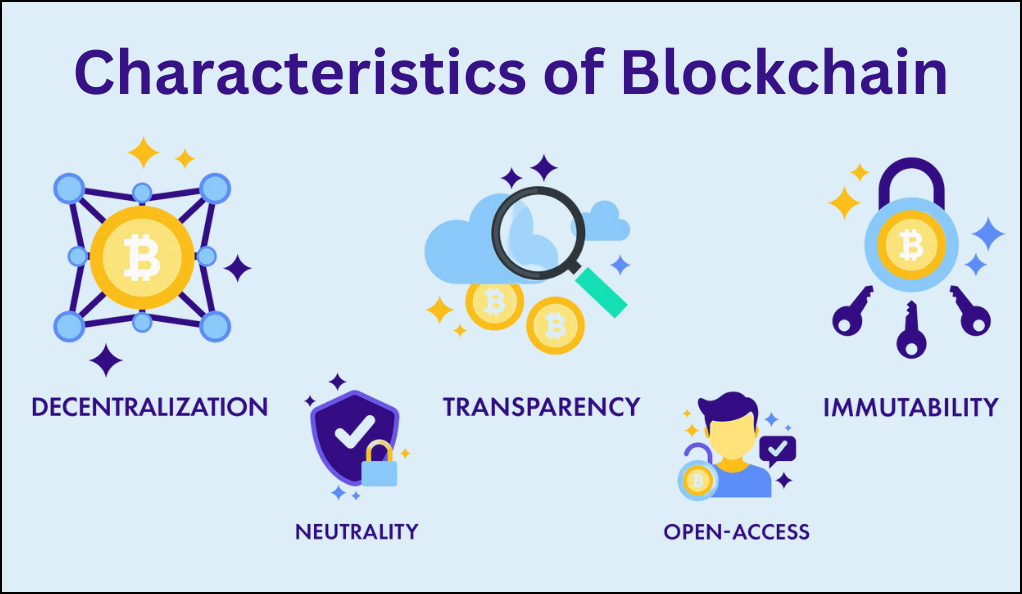
Key Features of Blockchain
Blockchain is distinguished by several foundational features that set it apart from traditional databases. One of its primary characteristics is decentralization, which means that unlike centralized systems where a single entity holds control, in blockchain, the control is distributed among all its participants. This ensures a more democratic and transparent system. Another defining feature is its inherent transparency. Every transaction made on the blockchain is visible to all its participants, fostering a sense of accountability and trust among users.
Additionally, the security of blockchain is unparalleled. All transactions are encrypted, safeguarding them from potential malicious attacks. Perhaps the most notable feature of blockchain is its immutability. Once data has been added to the blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to alter, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of the data. This combination of decentralization, transparency, security, and immutability makes blockchain a revolutionary tool in the digital realm.
Comparison Table: Centralized vs. Decentralized Systems
| Feature | Centralized Systems | Decentralized (Blockchain) Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Single entity | Distributed among participants |
| Security | Single point of failure | Enhanced security via encryption |
| Transparency | Limited; controlled access | High; all participants can view transactions |
| Alteration of Data | Possible | Nearly Impossible |
Significance of Blockchain
- Trustworthiness: Blockchain’s transparent nature ensures that all participants can trust the data and its source.
- Reduced Costs: By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain can significantly reduce transaction costs.
- Efficiency: Transactions are processed faster, especially cross-border ones, as they don’t require multiple intermediaries or lengthy verification processes.
- Innovation: The introduction of smart contracts on platforms like Ethereum has paved the way for decentralized applications (DApps) that can automate and streamline complex processes.
Real-world Applications of Blockchain
- Financial Services: From cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to decentralized finance platforms, blockchain is revolutionizing the financial sector.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain provides a transparent and tamper-proof record of product journeys from origin to consumer.
- Healthcare: Secure and efficient management of medical records, ensuring patient privacy and data integrity.
- Voting Systems: Transparent and tamper-proof voting systems that can potentially eliminate election fraud.
The Road Ahead: Challenges and Potential
While blockchain holds immense promise, it’s not without challenges. Scalability, energy consumption, and regulatory concerns are some of the hurdles it faces. However, with continuous research and innovations like the transition from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake, blockchain’s potential to revolutionize industries remains undiminished.
Data Analytics: The Powerhouse of Insights
In today’s digital age, where data is generated at an unprecedented rate, the ability to extract meaningful insights from this vast ocean of information is invaluable. Data analytics stands at the forefront of this endeavor, acting as a beacon that illuminates patterns, trends, and actionable insights from raw data.
Defining Data Analytics
Data analytics is the systematic computational analysis of data or statistics. It involves the use of specialized systems and software to convert raw data into meaningful information, which can then be used to make informed decisions, predict future trends, and identify areas of improvement.
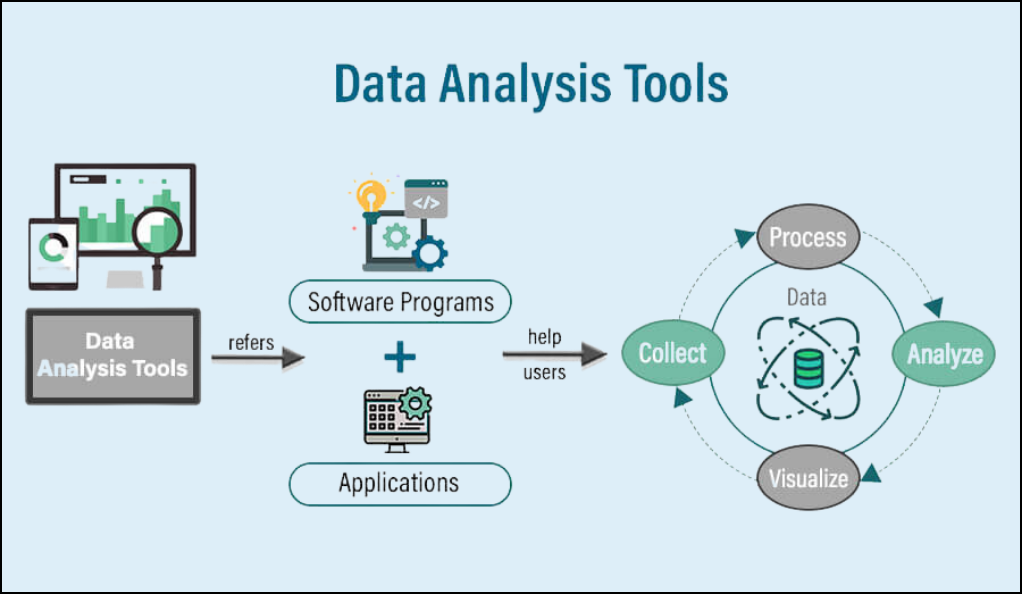
The Process of Data Analytics
- Data Collection: The first step involves gathering data from various sources, which could include databases, sensors, social media platforms, and more.
- Data Cleaning: Raw data often contains errors, duplicates, or irrelevant information. Cleaning ensures the data is accurate and ready for analysis.
- Data Analysis: Using statistical tools, algorithms, and machine learning techniques, the cleaned data is analyzed to extract insights.
- Data Visualization: The analyzed data is represented visually using charts, graphs, and other visualization tools to make the insights easily understandable.
Types of Data Analytics
- Descriptive Analytics: Focuses on understanding past data to analyze what happened.
- Diagnostic Analytics: Delves deeper into data to understand the cause of events.
- Predictive Analytics: Uses past data to predict future outcomes.
- Prescriptive Analytics: Recommends actions to take based on the analysis of past and predictive data.
Significance of Data Analytics
The significance of data analytics in today’s business landscape cannot be overstated. It plays a pivotal role in enabling businesses to make informed, data-driven decisions by providing a clear understanding of past trends and offering predictions for future ones.
Furthermore, data analytics aids in enhancing operational efficiency by pinpointing bottlenecks and inefficiencies in processes, allowing for timely optimization. By delving deep into customer behavior and preferences, analytics provides invaluable insights that can guide the development of better products and services tailored to meet customer needs.
Additionally, in an era where uncertainties abound, predictive analytics emerges as a crucial tool, empowering businesses to identify potential risks and devise strategies to mitigate them effectively. In essence, data analytics acts as a compass, guiding businesses towards informed strategies, innovation, and heightened operational efficiency.
Challenges in Data Analytics
While the benefits of data analytics are manifold, it’s not devoid of challenges. One of the primary concerns in the age of vast data collection is ensuring the privacy and security of user data. As businesses collect more information, the onus of safeguarding this data becomes paramount, especially in light of increasing cyber threats and stringent data protection regulations.
Additionally, the quality of data poses another significant challenge. Poor or inaccurate data can lead to misleading insights, which, in turn, can result in flawed decision-making. Moreover, as the sources and volumes of data continue to grow exponentially, the complexity of analyzing this data also escalates. This requires more sophisticated tools and expertise, adding layers of complexity to the analytical process. In essence, while data analytics offers a treasure trove of insights, navigating its challenges requires vigilance, expertise, and continuous adaptation to evolving technologies and regulations.
Synergy of Blockchain and Data Science
In the vast realm of technological advancements, two domains have emerged as particularly transformative: blockchain and data science. While each holds its own merit, their convergence promises a synergy that could redefine the future of digital innovation.
Understanding the Individual Powerhouses
- Blockchain: A decentralized ledger technology, blockchain ensures transparency, security, and immutability of data. It operates on consensus mechanisms, making alterations nearly impossible without the agreement of all participants.
- Data Science: A multidisciplinary field, data science employs scientific methods, algorithms, and systems to extract insights and knowledge from structured and unstructured data. It encompasses various subfields, including machine learning, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence.
The Convergence: How They Complement Each Other
- Data Integrity with Blockchain: Blockchain’s immutable nature ensures that the data fed into data science models is accurate and hasn’t been tampered with, leading to more reliable outcomes.
- Enhanced Security in Data Science: With blockchain, data used in data science models can be encrypted, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential and secure.
- Smart Contracts in Predictive Analysis: Using blockchain’s smart contracts, actions can be automatically triggered based on the outcomes of data science models, ensuring real-time responses.
Practical Applications of the Synergy
- Healthcare: Patient data can be securely stored on a blockchain, and data science can then analyze this data to predict disease outbreaks or recommend personalized treatments.
- Finance: Blockchain can ensure transparent and tamper-proof financial transactions, while data science can analyze these transactions to detect fraud or predict market trends.
- Supply Chain: Blockchain can track products from origin to consumer, and data science can optimize routes, predict demand, or ensure product quality.
Comparison Table: Individual vs. Combined Strengths
| Feature | Blockchain | Data Science | Synergy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Integrity | Ensures data hasn’t been altered | Relies on data accuracy | Guaranteed accurate data for analysis |
| Security | Encrypts data | Analyzes data | Encrypted data analysis |
| Automation | Uses smart contracts | Predictive modeling | Automated actions based on predictions |
| Scalability | Can be slow due to consensus | Can handle vast datasets | Efficient, secure handling of large datasets |
Challenges in Harnessing the Synergy
- Integration Complexity: Merging blockchain’s decentralized nature with data science tools can be technically challenging.
- Scalability Issues: Real-time data analysis combined with blockchain’s consensus mechanisms can sometimes slow down processes.
- Regulatory Concerns: Both fields are subject to evolving regulations, which can pose challenges in their combined application.
Impact of Blockchain on Data Science
The fusion of blockchain and data science is a testament to the rapid evolution of digital technologies. While both domains have individually transformed industries, their intersection is poised to redefine the paradigms of data management and analysis. Let’s delve into the profound impact of blockchain on the realm of data science.
The Foundation: Understanding Blockchain and Data Science
- Blockchain: At its core, blockchain is a decentralized ledger technology that ensures data immutability, transparency, and security. Transactions are recorded in blocks and linked in a chain, with each block being verified by network participants.
- Data Science: This is the art and science of extracting meaningful insights from vast and varied data sets. It employs algorithms, statistical methods, and machine learning techniques to analyze, interpret, and visualize data.
Enhancing Data Integrity and Trust
Blockchain’s immutable nature ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered without the consensus of the majority. This feature:
- Guarantees Data Authenticity: Data science models are only as good as the data they process. With blockchain, the integrity of data is assured, leading to more accurate and reliable analytical outcomes.
- Boosts Trust: Stakeholders can trust the analytical insights derived from blockchain-secured data, knowing that the data hasn’t been tampered with.
Secure Data Sharing and Collaboration
- Encrypted Data Transactions: Blockchain encrypts data transactions, ensuring that sensitive data remains confidential during analysis.
- Decentralized Data Pools: Multiple parties can contribute to decentralized data pools on blockchain platforms, fostering collaborative data science projects without compromising data security.
Real-time Analysis and Automated Responses
- Instantaneous Data Recording: As transactions are recorded in real-time on the blockchain, data scientists can access up-to-date data for real-time analysis.
- Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code can automatically trigger actions based on data science model outcomes, ensuring timely responses to insights.
Comparison Table: Data Science with and without Blockchain
| Feature | Traditional Data Science | Data Science with Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integrity | Can be compromised | Ensured by immutability |
| Data Security | Varies based on storage | Enhanced by encryption |
| Collaboration | Centralized databases | Decentralized data pools |
| Real-time Analysis | Depends on data update frequency | Enabled by real-time data recording |
Future Prospects and Industry Adoption
The rapid pace of technological advancements has ushered in a new era of innovation, with industries across the spectrum recognizing the potential of emerging technologies. As we stand on the cusp of a digital revolution, understanding the future prospects and the trajectory of industry adoption becomes paramount.
Technological Advancements on the Horizon
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is poised to become more integrated, with advancements in neural networks, deep learning, and natural language processing. The future may see AI systems that can think and reason like humans.
- Quantum Computing: With the potential to process complex computations in seconds, quantum computers could revolutionize industries like cryptography, medicine, and finance.
- 5G and Beyond: The rollout of 5G networks promises faster data speeds and lower latency, paving the way for real-time data processing and enhanced IoT capabilities.
Industry Adoption Trends
- Healthcare: From telemedicine to AI-driven diagnostics, the healthcare sector is undergoing a digital transformation, with technologies like blockchain ensuring data security and integrity.
- Finance: Fintech innovations, driven by AI, blockchain, and advanced analytics, are reshaping banking, investment, and insurance landscapes.
- Manufacturing: The rise of Industry 4.0, characterized by smart factories and IoT, promises increased automation and efficiency.
Comparison Table: Adoption Rate Across Industries
| Industry | Early Adopters (%) | Mainstream Adoption (%) | Future Potential (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | 45 | 30 | 25 |
| Finance | 50 | 35 | 15 |
| Manufacturing | 40 | 40 | 20 |
Challenges to Industry Adoption
- Infrastructure Limitations: For many emerging technologies, existing infrastructures might be inadequate, necessitating significant overhauls.
- Regulatory Hurdles: As technologies evolve, so must regulations. Striking a balance between innovation and regulation remains a challenge.
- Skill Gaps: The rapid pace of technological change means that there’s a constant need for upskilling and training.
The Road Ahead: Preparing for the Future
- Investment in R&D: Continuous research and development are crucial to stay ahead of technological curves.
- Collaborative Efforts: Industries, academia, and governments need to collaborate to ensure smooth technology adoption and integration.
- Ethical Considerations: As technologies advance, ethical considerations, especially in areas like AI, become paramount to ensure they benefit humanity as a whole.
Conclusion
As we navigate the dawn of a new technological epoch, the fusion of innovations like AI, quantum computing, and 5G is set to redefine the contours of industries globally. These advancements, while promising unparalleled efficiency and growth, also bring forth challenges that necessitate a harmonious blend of research, collaboration, and ethical considerations. The trajectory of industry adoption underscores a collective move towards a future that’s not just digitally-driven but also anchored in trust, security, and human-centric values. As industries, governments, and academia converge in their efforts, the horizon gleams with the promise of a world where technology doesn’t just augment reality but enriches the very fabric of our existence.
At bitvestment.software, our commitment is to deliver unbiased and reliable information on subjects like cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and stocks. It's crucial to understand that we are not equipped to offer financial advice, and we actively encourage users to conduct their own comprehensive research.
Read More