Introduction to Cryptocurrency Security

In the digital age, where cryptocurrencies have emerged as a revolutionary form of decentralized finance, the importance of security cannot be overstated. As the adoption of digital assets like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and countless altcoins continues to surge, so does the need for robust security measures to protect these assets. This section provides a comprehensive introduction to the world of cryptocurrency security, highlighting its significance and the foundational principles that every crypto enthusiast should be aware of.
The Digital Asset Landscape: A Brief Overview
Cryptocurrencies, often referred to as ‘digital assets’, are cryptographic tokens that exist on a blockchain. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (fiat currencies), cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized platforms. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Criteria | Traditional Fiat Currency | Cryptocurrency |
|---|---|---|
| Issuance | Centralized (Governments) | Decentralized (Blockchain) |
| Transaction Speed | Varies (Often slower) | Fast (Depends on the coin) |
| Anonymity | Low | High (Depends on the coin) |
| Physical Existence | Yes (Bills and coins) | No (Purely digital) |
Why is Security Paramount in the Crypto World?
- Irreversible Transactions: Unlike credit card chargebacks or bank reversals, cryptocurrency transactions are irreversible. Once confirmed, they cannot be undone. This makes it crucial to ensure security at every step.
- Anonymity and Pseudonymity: While cryptocurrencies offer a degree of privacy, this can also be a double-edged sword. If assets are stolen, tracking down the perpetrators can be challenging.
- Decentralized Nature: The decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies means there’s no central authority to oversee or regulate transactions. While this offers freedom from traditional banking systems, it also places the onus of security squarely on the user.
- Rising Value: With the increasing value of cryptocurrencies, they have become lucrative targets for cybercriminals. As the stakes get higher, the importance of security becomes paramount.
Foundational Principles of Cryptocurrency Security
- Personal Responsibility: In the crypto realm, the mantra is “Not your keys, not your coins.” Users must take personal responsibility for their private keys and wallets.
- Educate Before You Dive: Before investing or transacting in cryptocurrencies, it’s essential to educate oneself about potential risks and best practices.
- Stay Updated: The cryptocurrency landscape is rapidly evolving. Staying updated with the latest security measures and threats is crucial.
Understanding the Threat Landscape
As the popularity and adoption of cryptocurrencies grow, so does the attention they receive from potential adversaries. The threat landscape for digital assets is vast and ever-evolving, with cybercriminals employing a myriad of tactics to exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to users’ funds. This section delves deep into the common threats facing cryptocurrency users and provides real-world examples to underscore the importance of vigilance and proactive security measures.
Common Types of Cyber Threats Targeting Cryptocurrencies
- Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals create fake websites or emails that mimic legitimate cryptocurrency exchanges or wallet providers. Unsuspecting users might enter their credentials or private keys, giving attackers access to their funds.
- Ransomware: Malicious software that encrypts a user’s files or system, demanding a ransom (usually in cryptocurrency) to decrypt them.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Attackers intercept and potentially alter communications between two parties without their knowledge, often to steal login credentials or redirect funds.
- Exchange Hacks: Even though individual users might follow best practices, the exchanges where they trade or store their cryptocurrencies can be vulnerable. Over the years, several high-profile exchanges have been hacked, leading to significant losses.
- Cryptojacking: Attackers use a victim’s computer resources to mine cryptocurrencies without their consent.
- Sybil Attacks: In a Sybil attack, a single adversary controls multiple nodes in a network, primarily to subvert the network’s functionality.
Real-World Incidents and Their Implications
- The Mt. Gox Debacle: Once the world’s largest Bitcoin exchange, Mt. Gox filed for bankruptcy in 2014 after losing approximately 850,000 Bitcoins due to a prolonged hack. This incident underscored the importance of not storing large amounts of cryptocurrency on exchanges.
- The DAO Attack: The Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) was a complex smart contract on the Ethereum platform. In 2016, a vulnerability in its code was exploited, leading to a theft of 3.6 million Ether. This event led to a controversial hard fork in the Ethereum blockchain.
- Bitconnect Collapse: Touted as a lending platform, Bitconnect guaranteed high returns to its investors. However, in 2018, it abruptly shut down its exchange platform, leading to significant losses for many and highlighting the risks of investing in platforms with unclear business models.
Understanding these threats is the first step in safeguarding your assets. As we progress through this article, we’ll delve into specific strategies and tools you can employ to fortify your defenses and ensure your digital wealth remains secure.
The Basics of Crypto Wallet Security
Cryptocurrency wallets play a pivotal role in the digital asset ecosystem. They are the gatekeepers of your cryptocurrencies, allowing you to send, receive, and store your digital wealth. However, just as you wouldn’t leave your physical wallet carelessly lying around, it’s crucial to ensure that your crypto wallet is fortified against potential threats. This section delves into the different types of crypto wallets, their inherent risks, and best practices to secure them.
Different Types of Crypto Wallets: Hot vs. Cold
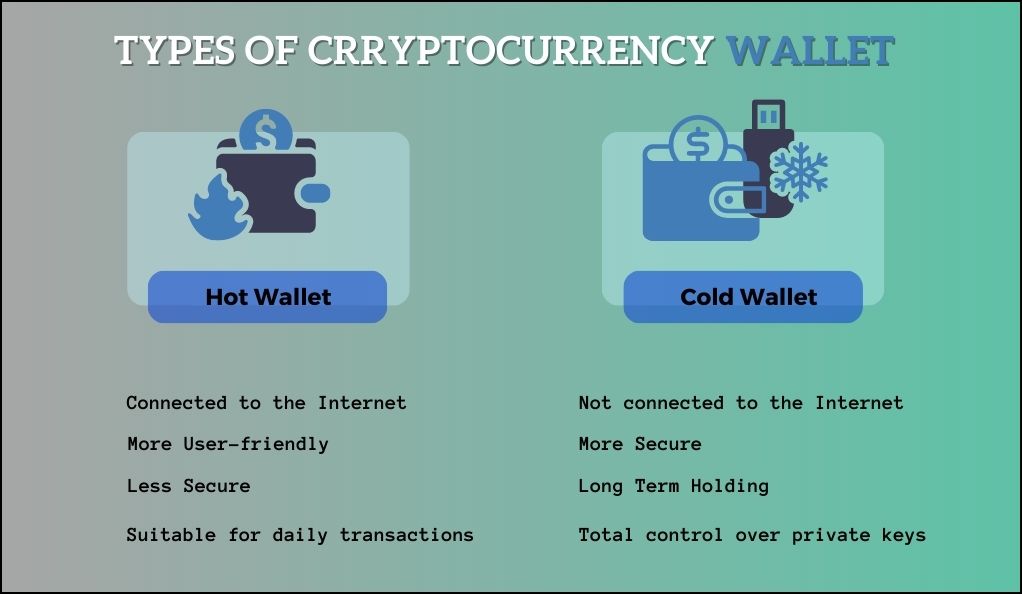
At a high level, cryptocurrency wallets can be categorized into two main types based on their connection to the internet:
- Hot Wallets (Online Wallets): These are wallets that are connected to the internet. They are convenient for frequent transactions but are vulnerable to online threats.
- Examples: Web wallets, exchange wallets, mobile wallets.
- Cold Wallets (Offline Wallets): These are wallets that are not connected to the internet, providing an added layer of security against online hacks.
- Examples: Hardware wallets, paper wallets.
| Wallet Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Wallet | – Instant access to funds – Suitable for daily transactions | – Vulnerable to online attacks – Dependency on third-party services |
| Cold Wallet | – Enhanced security – Total control over private keys | – Less convenient for frequent transactions – Risk of physical loss or damage |
Best Practices for Securing Your Crypto Wallets
- Private Key Management: Your private key is akin to the password to your bank account. Never share it with anyone, and avoid storing it online. If you lose control of your private key, you lose control of your funds.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your wallet to protect against data loss. Ensure that backups are stored in multiple secure locations.
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords: If your wallet has a password feature, use a strong, unique password. Consider using password managers to keep track of complex passwords.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): For hot wallets, especially those on exchanges, always enable MFA. This adds an additional layer of security, requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access.
- Stay Updated: Ensure that your wallet software is always updated to the latest version. Developers regularly release updates to fix vulnerabilities.
- Beware of Phishing: Always double-check URLs and email senders. Phishers often create websites that mimic legitimate platforms to steal your credentials.
- Consider Using Hardware Wallets: For significant amounts of cryptocurrencies, consider investing in a hardware wallet. These devices store your private keys offline, ensuring they remain out of reach from online attackers.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Its Role
In the vast and intricate world of digital security, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) stands out as one of the most effective measures to protect user accounts and data. MFA, as the name suggests, requires users to provide multiple forms of identification before granting access, adding an extra layer of security beyond just a password. In the context of cryptocurrency, where transactions are irreversible and stakes are high, the importance of MFA cannot be emphasized enough.
What is MFA and Why is it Crucial for Crypto Security?
MFA is a security system that requires more than one method of authentication from independent categories of credentials to verify the user’s identity. These methods can be:
- Something you know: This could be a password, PIN, or an answer to a “secret question.”
- Something you have: This might be a physical device like a security token, a smart card, or a smartphone.
- Something you are: This refers to biometrics, such as fingerprints, retina scans, or voice recognition.
In the realm of cryptocurrency, MFA plays a pivotal role for several reasons:
- Irreversible Transactions: As mentioned earlier, cryptocurrency transactions, once confirmed, cannot be undone. MFA ensures that even if a malicious actor gets hold of a user’s password, they would still need another form of authentication to access the funds.
- Rising Phishing Attacks: Phishing attacks, where attackers trick users into revealing their credentials, are on the rise. MFA acts as a deterrent, as having the password alone is not sufficient.
- Increased Value of Digital Assets: With the growing value and acceptance of cryptocurrencies, they have become prime targets for cybercriminals. MFA provides an additional security barrier, making unauthorized access considerably more challenging.
Setting Up MFA for Your Crypto Accounts
- Choose the Right Type of MFA: While SMS-based MFA is common, it’s not the most secure due to vulnerabilities like SIM swapping. Instead, consider using app-based MFA like Google Authenticator or Authy, or even hardware-based solutions like YubiKey.
- Regularly Backup Your MFA Codes: When setting up app-based MFA, you’ll often be provided with backup codes. Store these securely offline. They can be a lifesaver if you lose access to your MFA device.
- Stay Vigilant: Even with MFA enabled, always be cautious of phishing attempts. No legitimate service will ask you for your MFA codes outside of the login process.
- Use MFA Everywhere: While it’s crucial for crypto platforms, consider using MFA for all online services that offer it, from email accounts to social media. A breach in one account can sometimes lead to vulnerabilities in others.
Safeguarding Against Phishing and Scams
The allure of the digital gold rush brought about by cryptocurrencies has not only attracted genuine investors and enthusiasts but also a myriad of malicious actors looking to exploit the uninformed and the unsuspecting. Phishing and scams have become increasingly sophisticated, making it imperative for individuals to be well-informed and vigilant. This section aims to shed light on these deceptive tactics and provide guidance on how to steer clear of them.
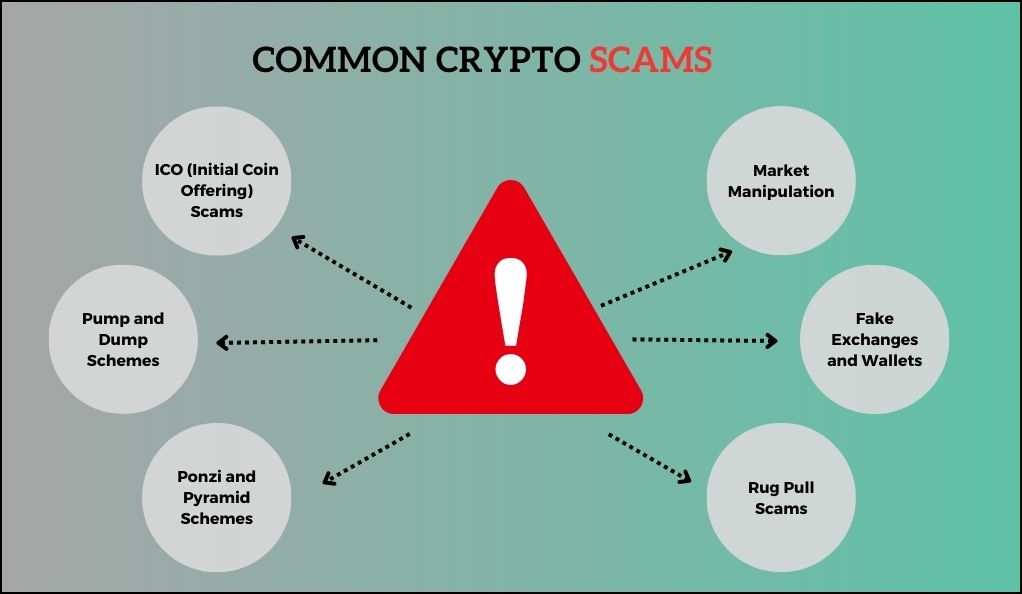
Recognizing Common Crypto Scams
- Fake Exchanges and Wallets: Scammers set up websites that mimic legitimate crypto exchanges or wallet providers. Users deposit funds, thinking they’re on a trusted platform, only to find their assets vanish.
- Ponzi and Pyramid Schemes: These schemes promise high returns to investors, but the profits are paid using the capital of newer participants. They collapse once new investments dry up, leading to significant losses for most participants.
- ICO (Initial Coin Offering) Scams: While many ICOs are legitimate, some are fraudulent. Scammers create fake projects, generate hype, collect funds, and then disappear.
- Pump and Dump Schemes: Groups artificially inflate the price of a cryptocurrency (pump) to attract unsuspecting investors. Once the price peaks, they sell off (dump), causing the price to plummet and leaving other investors at a loss.
Tips to Avoid Falling Victim to Phishing Attacks
- Check URLs Carefully: Always ensure you’re on the correct website. Look for ‘https’ in the URL and verify the domain name. Bookmarking essential sites can help.
- Beware of Unsolicited Communications: Be skeptical of emails, messages, or calls that claim to be from crypto services, especially if they ask for personal information or urge immediate action.
- Use Browser Extensions: Tools like MetaMask or EAL (EtherAddressLookup) can help identify and block malicious websites.
- Double-Check Wallet Addresses: Malware can change clipboard contents, so always double-check cryptocurrency addresses when sending funds.
- Stay Informed: Join crypto communities and forums. They can be valuable resources for staying updated on current scams and threats.
Protecting Your Investments
- Research Before Investing: Before diving into any investment, conduct thorough research. Check the project’s whitepaper, team, and community feedback.
- Avoid “Too Good to Be True” Offers: High returns with little to no risk are a red flag. If something sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
- Keep Personal Information Private: Never share sensitive information like your private key, seed phrase, or MFA codes.
The Role of Smart Contracts in Crypto Security
Smart contracts, a groundbreaking innovation brought to prominence by the Ethereum blockchain, have revolutionized the way we think about contractual agreements in the digital realm. These self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code lines can automate, decentralize, and secure various processes. However, as with any technology, they come with their own set of vulnerabilities. This section delves into the world of smart contracts, their potential security pitfalls, and how to ensure their robustness.
Understanding Smart Contracts and Their Vulnerabilities
At their core, smart contracts are programs that run on a blockchain. They automatically execute actions when certain conditions are met, without the need for intermediaries. While this automation offers efficiency and transparency, it also presents potential security challenges:
- Immutable Nature: Once deployed, a smart contract cannot be altered. This means that any vulnerability in the contract remains unless a new version is deployed.
- Complexity: The more complex a smart contract, the higher the chances of it having vulnerabilities. Simple oversights in code can lead to significant security breaches.
- Reentrancy Attacks: One of the most infamous vulnerabilities. An attacker can repeatedly call a function of the smart contract before its initial function call is finished, potentially draining funds.
- Gas Limitations: Every operation in a smart contract requires a certain amount of gas (fee). If a function requires more gas than provided, it fails, potentially causing unexpected behavior.
Ensuring the Security of Smart Contracts
- Thorough Auditing: Before deploying, smart contracts should undergo rigorous auditing by experts. This helps identify and rectify potential vulnerabilities.
- Use Established Patterns: Instead of writing contract code from scratch, using well-established patterns and libraries can reduce the risk of vulnerabilities.
- Limit Contract Complexity: Keeping contracts simple and modular makes them easier to audit and reduces the chances of overlooked vulnerabilities.
- Stay Updated: The world of blockchain and smart contracts is rapidly evolving. Developers should stay updated with the latest best practices and potential vulnerabilities.
Real-world Implications: The DAO Attack Revisited
The DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) attack remains one of the most significant events highlighting smart contract vulnerabilities. An attacker exploited a reentrancy vulnerability, siphoning off a third of the DAO’s funds. This led to a hard fork in Ethereum, creating two separate chains: Ethereum (ETH) and Ethereum Classic (ETC). The incident underscores the importance of smart contract security in maintaining trust and functionality in the crypto ecosystem.
Backup and Recovery: Preparing for the Worst
In the volatile world of cryptocurrencies, where the stakes are high and the landscape is ever-evolving, the importance of backups and recovery cannot be stressed enough. While security measures aim to prevent breaches and unauthorized access, backups act as a safety net, ensuring that even in the face of unexpected events, your digital assets remain accessible. This section delves into the significance of backups in the crypto realm and offers guidelines on how to securely backup and recover your digital assets.
Importance of Backups in the Crypto World
- Irreversible Transactions: As reiterated throughout this guide, cryptocurrency transactions, once executed, are irreversible. A simple mistake, like sending funds to the wrong address, can result in permanent loss. Backups ensure you have access to your assets even if you make errors or face technical issues.
- Device Failures: Computers, smartphones, and hardware wallets are not infallible. They can malfunction, get stolen, or face other unforeseen issues. Backups act as a contingency plan, ensuring continuous access to your assets.
- Human Errors: Accidental deletions, overwrites, or other inadvertent actions can compromise your digital assets. With a proper backup, such errors become rectifiable.
Steps to Securely Backup and Recover Your Digital Assets
- Multiple Backups: Don’t rely on a single backup. Create multiple copies and store them in different physical locations. This diversification reduces the risk of total loss due to events like natural disasters.
- Cold Storage: Consider using cold storage solutions, like paper wallets or air-gapped computers, for backups. These offline methods ensure that your backup remains safe from online threats.
- Encrypt Your Backups: Ensure that your backups are encrypted. This adds an additional layer of security, preventing unauthorized access even if someone gets hold of the backup.
- Regularly Test Recovery: A backup is only as good as its recovery process. Regularly test the recovery of your assets using the backup to ensure it’s functional and up-to-date.
- Update Backups After Each Transaction: Cryptocurrency wallets generate new addresses for each transaction. Regularly update your backups to ensure they reflect the most recent changes.
- Secure Physical Backups: If you’re using physical backups like paper wallets, ensure they’re stored in secure locations like safes or safety deposit boxes. Consider using tamper-evident bags or seals.
- Beware of Cloud Storage: While cloud storage is convenient, it’s also vulnerable to hacks and breaches. If you must use cloud storage, ensure the backup is heavily encrypted and consider it as just one of multiple backup solutions.
Advanced Security Measures for the Tech-Savvy
While the foundational security measures are essential for all cryptocurrency users, those who are more technically inclined or possess significant digital assets might seek additional layers of protection. This section delves into advanced security measures that, while potentially more complex, offer heightened security for your digital wealth.
Using Hardware Wallets and Air-Gapped Computers
- Hardware Wallets: These are physical devices designed to securely store cryptocurrency private keys. They ensure that private keys never leave the device, making transactions secure even on compromised computers.
- Popular Choices: Ledger Nano S, Trezor, and KeepKey.
- Advantages: Immune to viruses, phishing attacks, and most forms of malware. They require physical confirmation for transactions, adding an extra layer of security.
- Air-Gapped Computers: An air-gapped computer is never connected to the internet, ensuring it remains isolated from online threats. Users can sign transactions on the air-gapped computer and then transfer them to an online device for broadcasting.
- Usage: Ideal for storing large amounts of cryptocurrencies or for those particularly concerned about potential malware or hacks.
Exploring Decentralized Identity Solutions
Decentralized identity solutions aim to give users control over their personal data, eliminating the need for centralized entities. In the context of cryptocurrency:
- Self-Sovereign Identity: Users have complete control over their identity data without relying on any centralized authority. This reduces the risk of massive data breaches.
- Blockchain-Based Authentication: Instead of traditional username-password systems, blockchain-based solutions can provide cryptographic proof of identity, enhancing security.
Multi-Signature Wallets
A multi-signature (multi-sig) wallet requires multiple private keys to authorize a transaction. It’s akin to a bank safe deposit box that requires two keys to open.
- Usage: Ideal for organizations or partnerships where funds should only be moved with consensus.
- Security Implication: Even if a malicious actor gains access to one private key, they cannot move funds without the other required keys.
Regularly Monitor and Audit Smart Contracts
For those involved in creating or investing in decentralized applications (DApps) or platforms:
- Continuous Auditing: Regularly audit smart contracts for vulnerabilities. New potential threats emerge as the ecosystem evolves.
- Use Monitoring Tools: Tools like Mythril or Oyente can help in identifying vulnerabilities in smart contracts.
Emerging Technologies and the Future of Cryptocurrency Security
The world of cryptocurrency is in a constant state of flux, driven by technological advancements and the relentless pursuit of enhanced security. As cyber threats evolve, so too do the defenses against them. This section offers a glimpse into the emerging technologies shaping the future of cryptocurrency security and how they promise to fortify the digital asset landscape.
Quantum Computing and Cryptocurrency
- The Threat: Quantum computers, with their ability to process complex calculations at unprecedented speeds, pose a potential threat to the cryptographic algorithms that underpin cryptocurrencies. They could, theoretically, break the encryption of public-key cryptosystems, allowing malicious actors to derive private keys from public ones.
- The Defense: Cryptographers are already working on post-quantum cryptographic algorithms that would be resistant to quantum attacks. Transitioning to quantum-resistant algorithms will be crucial in the coming years.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
- Enhanced Security: Unlike centralized exchanges, which are prime targets for large-scale hacks, DEXs operate without a central authority. This decentralized nature reduces the risk of massive fund losses.
- User Control: On DEXs, users retain control of their private keys, ensuring that they have full ownership of their assets at all times.
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions and Security
- What Are They? Layer 2 solutions, like the Lightning Network for Bitcoin or Plasma for Ethereum, aim to scale blockchains by handling transactions off the main chain.
- Security Implications: While these solutions offer faster and cheaper transactions, they come with their own set of security considerations. Continuous monitoring and updates will be essential to ensure these off-chain solutions remain secure.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Crypto Security
- Predictive Analysis: AI can analyze vast amounts of data to predict potential security threats or suspicious activities, allowing for proactive defense measures.
- Automated Threat Response: In the event of a security breach, AI-driven systems can initiate immediate automated responses, minimizing potential damage.
- Smart Contract Analysis: AI can be used to analyze smart contracts, identifying vulnerabilities or malicious code more efficiently than manual audits.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs
- Enhanced Privacy: Technologies like zk-SNARKs allow for transaction validation without revealing transaction details, enhancing privacy.
- Security Implications: While zero-knowledge proofs offer enhanced privacy, they also introduce new complexities, requiring rigorous auditing and testing to ensure security.
The future of cryptocurrency security is a blend of challenges and innovations. As threats evolve, the crypto community continues to rally, developing cutting-edge solutions to safeguard digital assets. By staying informed and embracing these emerging technologies, users can navigate the crypto landscape with confidence and security.
Conclusion
In the digital age, where cryptocurrencies have emerged as both a revolutionary form of currency and a lucrative investment, the importance of security cannot be overstated. As we’ve journeyed through the multifaceted landscape of cryptocurrency security, it’s evident that safeguarding digital assets requires a blend of foundational knowledge, proactive measures, and an understanding of emerging technologies. From the basics of wallet security to the advanced realms of quantum resistance and AI-driven defenses, the crypto world offers both challenges and solutions in equal measure.
The rapid evolution of the cryptocurrency ecosystem, coupled with its decentralized nature, means that responsibility largely rests on individual users. By staying informed, leveraging both established and cutting-edge security practices, and maintaining a healthy skepticism, users can navigate this dynamic landscape with confidence. It’s a world where the promise of decentralized finance and autonomy goes hand in hand with the imperative of vigilance and continuous learning.
In conclusion, as the world of cryptocurrencies continues to expand and integrate into mainstream finance and daily life, its security will remain paramount. The fusion of technology, community collaboration, and individual responsibility will be the cornerstone of ensuring that this digital frontier remains both innovative and secure for all its participants.
At bitvestment.software, our commitment is to deliver unbiased and reliable information on subjects like cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and stocks. It's crucial to understand that we are not equipped to offer financial advice, and we actively encourage users to conduct their own comprehensive research.
Read More