Cryptocurrencies, often hailed as the money of the future, have a relatively short but impactful history. The concept of a decentralized digital currency can be traced back to the late 1970s and 1980s with the introduction of cryptographic electronic money like eCash. However, the true revolution began in 2009 with the introduction of Bitcoin by an anonymous entity known as Satoshi Nakamoto.
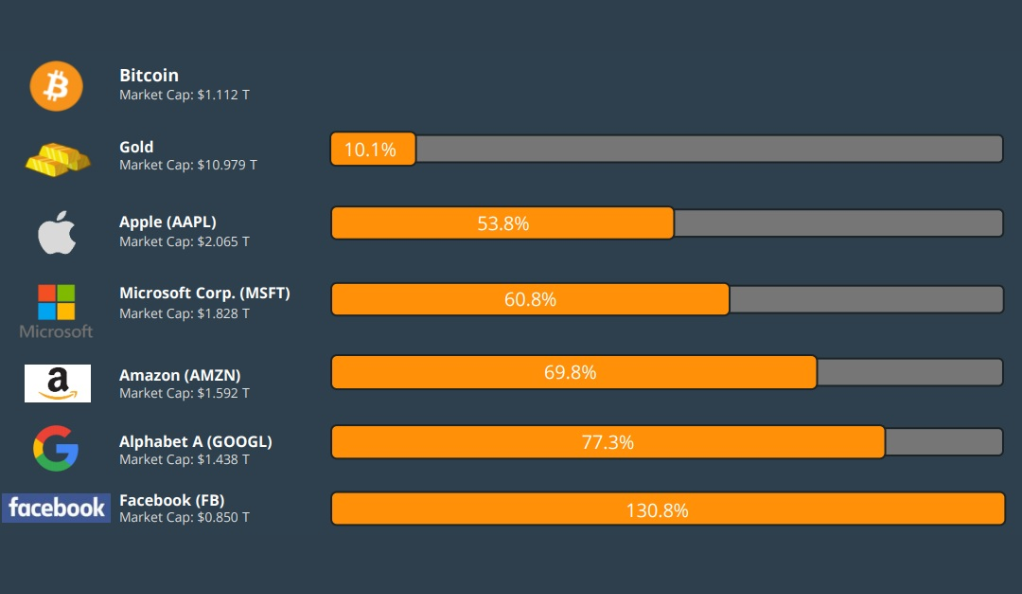
The Trillion-Dollar Industry: Bitcoin and Its Counterparts
Bitcoin, the pioneer of the cryptocurrency movement, was the first to solve the double-spending problem without the need for a central authority or server. Its decentralized nature, combined with its finite supply and blockchain technology, made it a unique and attractive investment opportunity. As of its peak, Bitcoin’s market capitalization surpassed $1 trillion, solidifying its position as the leading cryptocurrency.
However, Bitcoin isn’t alone in this vast digital ocean. Hundreds of other cryptocurrencies, often referred to as ‘altcoins’, have emerged, each with its unique features and purposes. Ethereum, for instance, introduced the world to smart contracts and decentralized applications, while Ripple aimed to revolutionize real-time cross-border payments.
Decentralization: The Core Principle
One of the foundational principles of cryptocurrencies is decentralization. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments and centralized institutions, cryptocurrencies operate on a decentralized network of computers. This decentralization ensures that no single entity has control over the currency, making it immune to government interference or manipulation.
Section Breakdown: How Decentralization Works
- Peer-to-Peer Network: Every transaction occurs directly between users without an intermediary.
- Blockchain Technology: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain. This ledger is maintained by nodes or computers in the network.
- Consensus Mechanisms: For a transaction to be added to the blockchain, network participants must agree on its validity. Common consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
The Democratizing Force of Cryptocurrencies
Power Shift from Central Banks and Wall Street
For centuries, the global financial system has been anchored by centralized institutions such as central banks, major financial corporations, and Wall Street. These entities have held significant sway over monetary policies, interest rates, and financial regulations. However, the advent of cryptocurrencies has begun to challenge this long-standing status quo.
Cryptocurrencies, by their very nature, are decentralized. This means they operate outside the traditional banking system, offering a level of financial freedom and autonomy previously unavailable to the average individual. No longer are financial transactions solely at the mercy of banking hours, hefty transaction fees, or national borders. With cryptocurrencies, funds can be sent and received anywhere in the world, at any time, often with minimal fees.
Global Embrace and Resistance: The Regulation Dynamics
As cryptocurrencies gained popularity, they caught the attention of regulators worldwide. Their decentralized nature posed both opportunities and challenges for governments and financial institutions.
Table 2: Global Cryptocurrency Regulation Overview
| Country | Stance on Cryptocurrencies | Key Regulations/Decisions |
|---|---|---|
| USA | Cautiously Optimistic | SEC’s increasing oversight on Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) |
| China | Restrictive | Banned all crypto transactions and mining in 2021 |
| Japan | Welcoming | Recognized Bitcoin as a legal payment method in 2017 |
| India | Mixed | Fluctuating stances, with proposals to launch its own digital currency |
While some countries, like Japan, have embraced cryptocurrencies and integrated them into their financial ecosystems, others, like China, have taken a more restrictive approach. The motivations behind these regulatory decisions vary, from concerns over potential illicit activities to the desire to protect national currencies.
However, it’s undeniable that these regulations have a significant impact on the global cryptocurrency market. For instance, when China announced its ban on crypto transactions and mining, the global cryptocurrency market experienced a sharp decline, underscoring the influence of regulatory decisions on market dynamics.
The Promise of Financial Inclusion
One of the most profound impacts of cryptocurrencies is their potential to foster financial inclusion. Billions of people worldwide lack access to traditional banking services, either due to geographical constraints, lack of proper documentation, or financial barriers. Cryptocurrencies can bridge this gap.
With just a smartphone and an internet connection, anyone can create a cryptocurrency wallet, allowing them to send, receive, and store funds. This democratization of finance can empower individuals in developing nations, giving them access to global markets and the ability to participate in the digital economy.
Cryptocurrencies: Beyond Just Money
The Multifaceted Nature of Digital Assets
While the primary function of cryptocurrencies is to serve as a medium of exchange, their potential extends far beyond simple transactions. Built on the backbone of blockchain technology, these digital assets have found applications in various sectors, revolutionizing traditional systems and processes.
Digital Real Estate: The Virtual Frontier
The concept of owning land and property has taken a digital turn with the rise of virtual real estate. Platforms like Decentraland and Cryptovoxels allow users to purchase, develop, and sell parcels of land in a virtual environment. These virtual spaces can host games, art galleries, and even business meetings.
Table 3: Popular Virtual Real Estate Platforms
| Platform | Description | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|
| Decentraland | A decentralized virtual world | User-owned content, marketplace for assets |
| Cryptovoxels | A virtual city built on the Ethereum blockchain | Virtual art galleries, interactive spaces |
| Somnium Space | Immersive VR world | Land ownership, VR meetings, and events |
Cryptocurrencies in Software Development
The software industry has also felt the impact of cryptocurrencies. Developers can now be compensated in cryptocurrencies for their contributions to open-source projects. Platforms like Gitcoin facilitate this, linking developers with projects and ensuring fair compensation using digital currencies.
Cryptocurrencies and the Arts
The art world has been revolutionized by the concept of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). Artists can now tokenize their work, ensuring authenticity and ownership. This has opened up new revenue streams for artists, allowing them to sell their creations directly to enthusiasts without intermediaries.
The Dark Side: Illicit Activities
Cryptocurrencies, due to their pseudonymous nature, have unfortunately also been associated with illegal activities. Darknet markets have emerged where users can purchase prohibited items using digital currencies. While this represents a small fraction of cryptocurrency transactions, it’s an aspect that has drawn significant attention and concern.
The Global Response: Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
The Rise of CBDCs in Response to the Cryptocurrency Boom
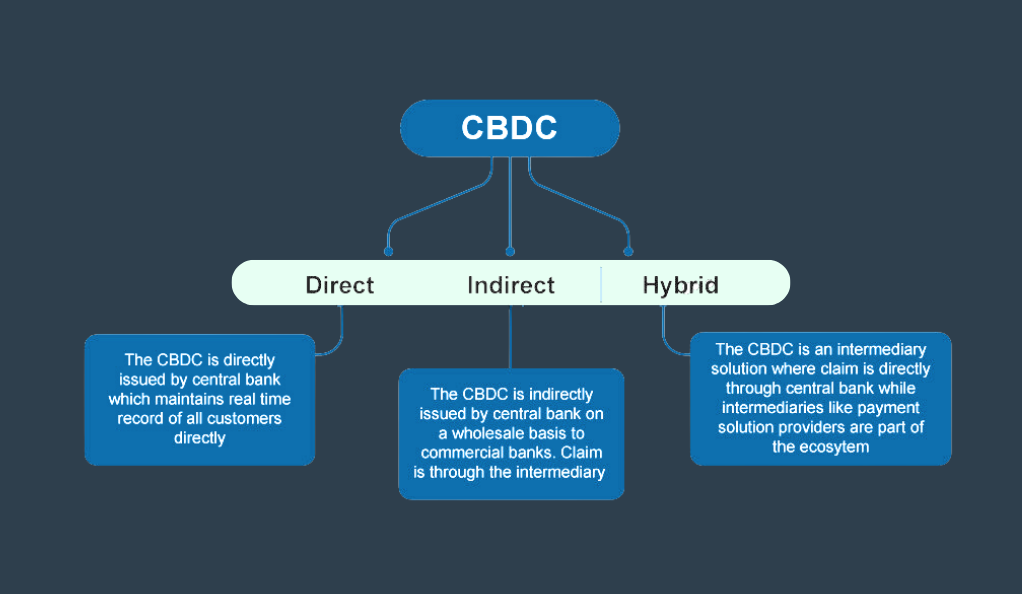
As the popularity and adoption of cryptocurrencies surged, central banks worldwide began to take notice. Concerned about the potential implications for monetary policy, financial stability, and the traditional banking system, many central banks started exploring the idea of issuing their own digital currencies. These Central Bank Digital Currencies, or CBDCs, represent a fusion of traditional fiat currencies with blockchain technology, aiming to offer the best of both worlds.
Why Central Banks are Considering CBDCs
Several factors have driven central banks to consider the development and issuance of CBDCs:
- Financial Inclusion: CBDCs can provide a digital payment method for those without access to traditional banking.
- Efficiency and Security: Digital currencies can offer faster, cheaper, and more secure payment systems.
- Monetary Policy Implementation: CBDCs can provide central banks with new tools for implementing monetary policy.
- Counteracting Private Digital Currencies: With the rise of cryptocurrencies and stablecoins, CBDCs can act as a counterbalance, ensuring state control over the monetary system.
Challenges and Concerns with CBDCs
While CBDCs offer numerous benefits, they also come with challenges:
- Privacy Concerns: Unlike decentralized cryptocurrencies, CBDCs could allow central banks to monitor transactions, raising privacy issues.
- Impact on Traditional Banks: With direct access to central bank money, the role of commercial banks might diminish.
- Technological Challenges: Implementing a secure and efficient CBDC system requires robust technology and infrastructure.
The Balance Between Innovation and Control
The introduction of CBDCs represents a delicate balance for central banks. On one hand, they aim to harness the benefits of digital currencies, such as increased efficiency and financial inclusion. On the other, they seek to maintain control over the monetary system, ensuring stability and trust.
Challenges and Criticisms
The Environmental Impact of Cryptocurrency Mining
One of the most significant criticisms directed at cryptocurrencies, particularly Bitcoin, is the environmental impact of its mining process. The Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, used by Bitcoin and several other cryptocurrencies, requires vast amounts of computational power. This, in turn, consumes a tremendous amount of electricity.
Concerns Over Illicit Activities
Cryptocurrencies, due to their pseudonymous nature, have been linked to various illicit activities, including money laundering, tax evasion, and illegal trade on the dark web. While a vast majority of cryptocurrency transactions are legitimate, these negative associations have led to increased scrutiny and calls for regulation.
Volatility: A Double-Edged Sword
The price volatility of cryptocurrencies is another major concern. While this volatility can lead to significant profits for investors, it also introduces a level of risk that can result in substantial losses. This unpredictability makes many hesitant to adopt cryptocurrencies as a regular medium of exchange.
Regulatory and Security Concerns
As cryptocurrencies grow in popularity, they attract the attention of regulators worldwide. The lack of a standardized regulatory framework can lead to uncertainties for investors and users. Additionally, while blockchain technology is inherently secure, exchanges and wallets can be vulnerable to hacks, leading to significant losses for users.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): The New Financial Ecosystem
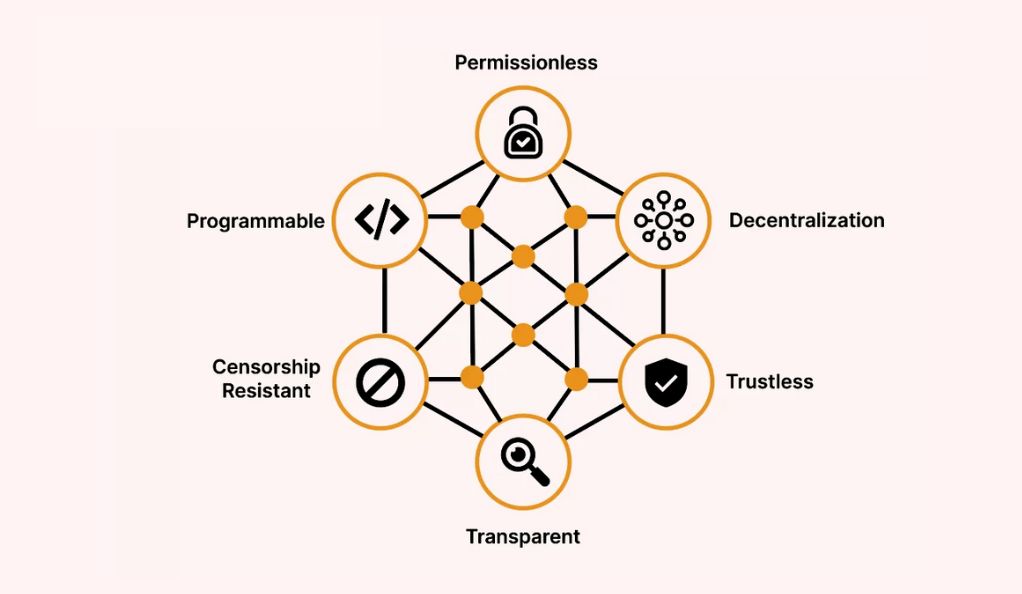
Decentralized Finance, commonly known as DeFi, represents a paradigm shift in the financial world. At its core, DeFi aims to recreate traditional financial systems (like lending, borrowing, and trading) using blockchain technology, eliminating intermediaries and offering more open, accessible, and efficient financial services.
The Building Blocks of DeFi
DeFi operates on a series of smart contracts, primarily on the Ethereum blockchain. These contracts are self-executing, with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
Key Components of DeFi:
- Lending Platforms: Allow users to lend or borrow funds without banks. Examples include Compound and Aave.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Platforms where users can trade cryptocurrencies without a centralized authority. Uniswap and SushiSwap are popular DEXs.
- Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies pegged to stable assets like the US Dollar. USDC and DAI are examples.
- Yield Farming: A strategy where users lock up their funds in a DeFi protocol to earn rewards.
Benefits of DeFi
Accessibility: DeFi platforms are open to anyone with an internet connection, democratizing access to financial services.
Transparency: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger, ensuring transparency and trust.
Interoperability: DeFi protocols can easily integrate with other services, creating a connected financial ecosystem.
Custody: Users have full control over their funds, reducing the risk of centralized breaches.
Challenges Facing DeFi
Despite its potential, DeFi is not without challenges:
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Being code-based, smart contracts can have bugs or vulnerabilities that can be exploited.
- High Gas Fees: Especially on the Ethereum network, transaction fees can be high, deterring users.
- Lack of Regulation: The decentralized nature of DeFi makes it hard to regulate, leading to potential risks for users.
The Future of DeFi
The DeFi sector is rapidly evolving, with new projects and innovations emerging regularly. As the technology matures and becomes more user-friendly, it’s anticipated that DeFi will play a significant role in reshaping the global financial landscape. From decentralized insurance to peer-to-peer lending, the possibilities are vast and transformative.
The Road Ahead: Predictions and Possibilities
As we’ve journeyed through the world of cryptocurrencies, it’s evident that they represent more than just a speculative bubble or a fleeting trend. With deep-rooted technological foundations and transformative applications across various sectors, cryptocurrencies are poised to play a significant role in the future of finance and beyond.
Global Acceptance on the Horizon
While cryptocurrencies have already achieved a considerable degree of acceptance, the future might see them becoming as ubiquitous as traditional currencies. As regulatory frameworks become more defined and the technology becomes more user-friendly, it’s plausible to envision a world where paying with Bitcoin or Ethereum becomes as commonplace as using dollars or euros.
Integration with IoT and Smart Cities
The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly transforming our world, with devices, vehicles, and even cities becoming interconnected. Cryptocurrencies, with their decentralized and secure nature, could play a pivotal role in this ecosystem. Imagine self-driving cars that pay for their own charging using cryptocurrencies or smart homes that autonomously handle all financial transactions, from paying utility bills to ordering groceries.
The Evolution of Financial Institutions
As DeFi continues to grow, traditional financial institutions might need to adapt or risk becoming obsolete. Banks could evolve into hybrid entities, integrating blockchain technology and offering both traditional and crypto-related services. We might also see the rise of entirely new financial entities, born from the fusion of DeFi and traditional finance.
Regulatory Landscape: A Balancing Act
The future will undoubtedly see more defined and possibly stricter regulations surrounding cryptocurrencies. Governments and regulatory bodies will face the challenge of creating frameworks that ensure safety and transparency without stifling innovation. Collaborative efforts between the crypto industry and regulators could lead to a harmonious coexistence.
The Potential of Untapped Use Cases
While we’ve already seen diverse applications of cryptocurrencies, the future might unveil use cases we haven’t even imagined yet. From revolutionizing supply chain management to creating entirely new economic models, the possibilities are vast and exciting.
Conclusion
As we navigate the intricate tapestry of the cryptocurrency landscape, it’s evident that we stand at the nexus of innovation and transformation. Cryptocurrencies, with their decentralized ethos and groundbreaking technology, are not merely reshaping the contours of finance but are also redefining our understanding of trust, autonomy, and digital collaboration. While challenges persist, the potential for a more inclusive, transparent, and efficient global financial ecosystem is within reach. As we look to the horizon, it’s imperative to approach this digital frontier with both caution and optimism, recognizing that we are participants in crafting the financial narrative of the future.
At bitvestment.software, our commitment is to deliver unbiased and reliable information on subjects like cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and stocks. It's crucial to understand that we are not equipped to offer financial advice, and we actively encourage users to conduct their own comprehensive research.
Read More